Our Latest Posts

What Defines a Medicinal Herb?

A medicinal herb is any plant that contains bioactive phytochemicals capable of influencing biological functions. These compounds work either alone or in synergy to provide therapeutic effects. Some of the most important categories include:
Alkaloids (e.g., morphine from Papaver somniferum): Powerful effects on the nervous system.
Flavonoids and Polyphenols (e.g., quercetin, catechins): Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents.
Terpenoids (e.g., menthol, artemisinin): Broad roles in antimicrobial and metabolic regulation.
Essential Oils (e.g., thymol from thyme, eugenol from clove): Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and aromatic properties.
Saponins and Glycosides (e.g., digoxin from Digitalis): Cardioactive and immunomodulatory effects.
Therapeutic Categories of Medicinal Herbs
Medicinal herbs can be grouped by their primary therapeutic actions:

Anti-inflammatory Herbs
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa) curcumin reduces inflammation linked to arthritis and chronic diseases.
- Boswellia serrata resins with anti-arthritic effects.

Adaptogens (Stress & Energy Regulators)
- Panax ginseng boosts energy, immunity, and cognitive performance.
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) reduces stress and supports hormonal balance.

Immune-Boosting Herbs
- Echinacea purpurea enhances immune response against respiratory infections.
- Astragalus membranaceus widely used in TCM for immune and anti-fatigue effects.

Cardiovascular Herbs
- Garlic (Allium sativum) lowers blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) supports heart function and circulation.

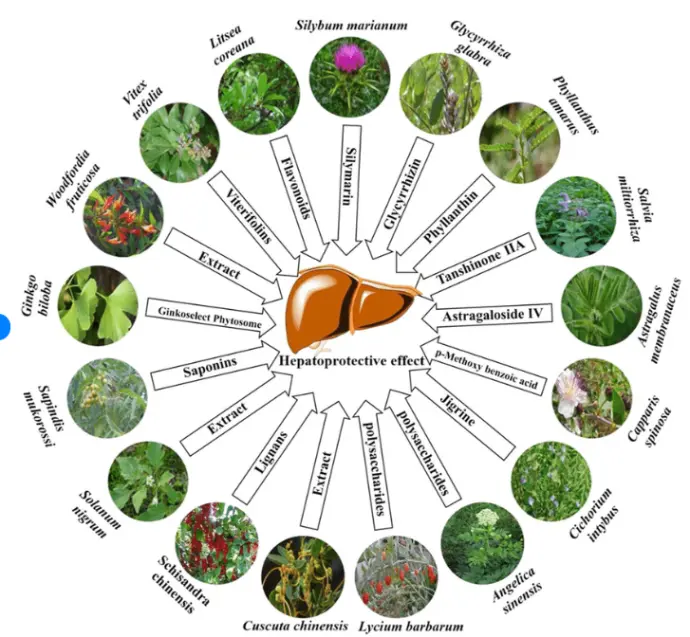
Digestive and Liver-Supporting Herbs
- Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) protects liver cells and aids detoxification.
- Peppermint (Mentha piperita) relieves indigestion and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
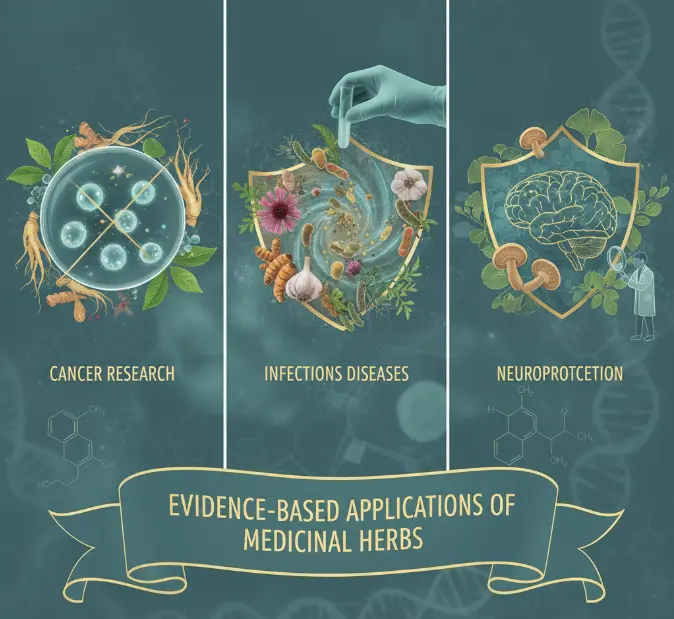
Evidence-Based Applications
Scientific studies have confirmed several important roles of medicinal herbs in modern healthcare:
- Cancer Research: Compounds from Moringa oleifera, Green tea (Camellia sinensis), and Turmeric show promise in modulating oxidative stress and inhibiting tumor growth.
- Infectious Diseases: Artemisinin from Artemisia annua revolutionized malaria treatment. Garlic and ginger demonstrate antimicrobial activity against bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
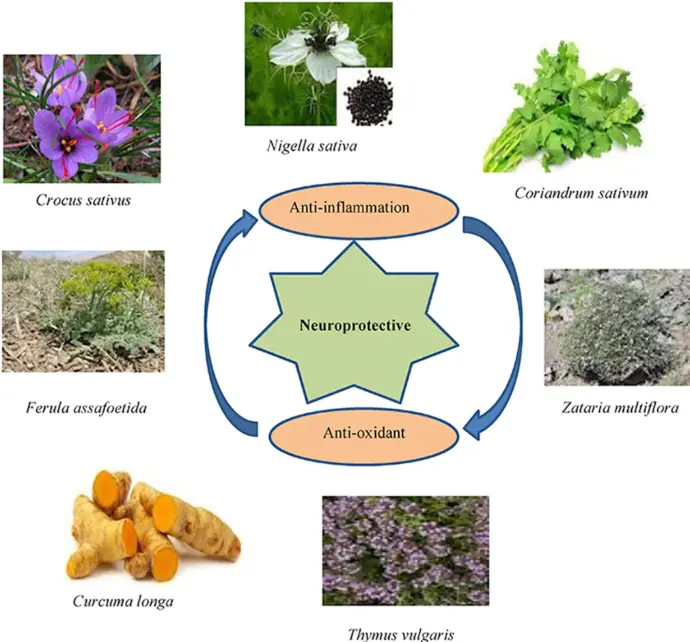
- Neuroprotection: Ginkgo biloba extracts may improve circulation to the brain, supporting memory and cognitive function in aging populations.